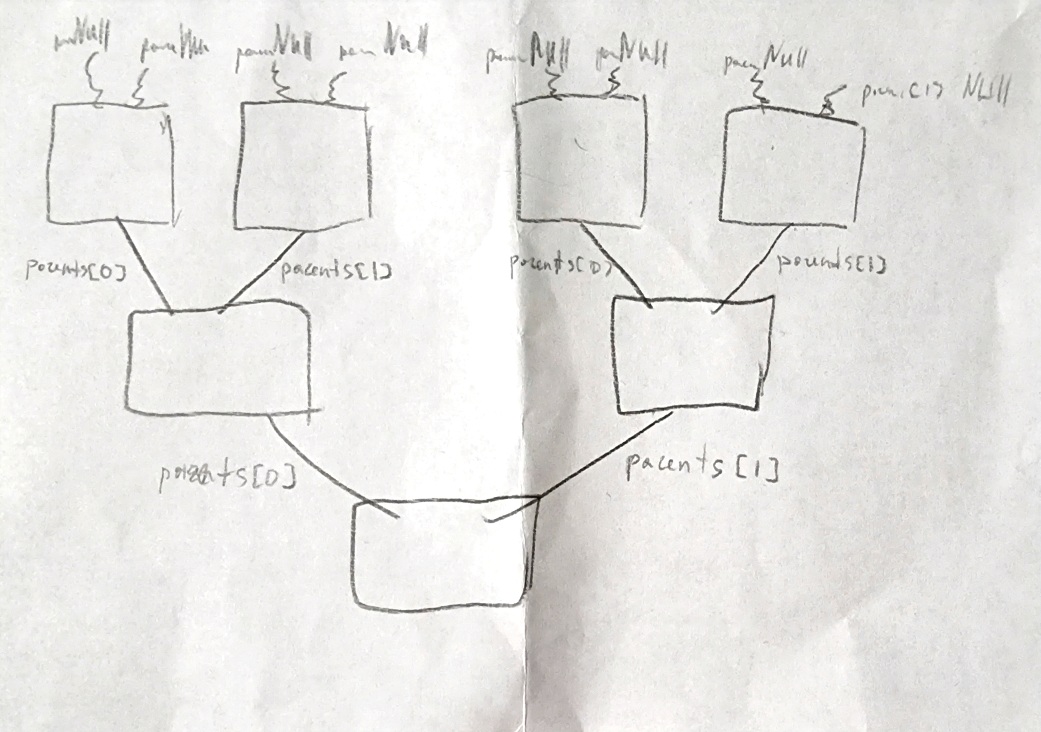
На пятой неделе курса Computer Science — CS50 (Harvard) мы изучили структуры данных и научились обращаться к элементам структур по их адресу. Чтобы выполнить домашнее задание (лабораторная работа 5 — inheritance.c), нужно разобраться в научном принципе наследования группы крови от родителей к детям. Задача: написать программу, которая запускает симуляцию семьи из трех поколений и присваивает каждому ее члену группу крови на основании группы крови родителей.
Как наследуется группа крови:
- есть всего три возможных формы гена (их называют «аллель» или строительный блок), определяющих тип группы крови — это A, B, и O;
- сама группа крови — это всегда два аллеля (всевозможные комбинации A, B, и O), например, AO, AA, OB и т.д.;
- группа крови «передается» от родителей к ребенку следующим образом: от каждого родителя случайным образом отбирается один аллель и затем они объединяются в новую пару — это и есть группа крови ребенка (например, у родителей было AO и OB -> у ребенка может быть AB, OO, OB или AO).
В нашем задании нужно каждому ребенку присвоить по два родителя, и так для трех поколений. То есть в младшем поколении есть ребенок, у него есть мама и папа. У мамы и папы тоже есть свои мамы и папы. Семья создается при помощи структуры. Нам предложен код программы, где пропущены функции для создания семьи и последующей очистке памяти.
Код программы (Игроглаз)
// Simulate genetic inheritance of blood type
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
// Each person has two parents and two alleles
typedef struct person
{
struct person *parents[2];
char alleles[2];
}
person;
const int GENERATIONS = 3;
const int INDENT_LENGTH = 4;
person *create_family(int generations);
void print_family(person *p, int generation);
int free_family(person *p);
char random_allele();
int main(void)
{
// Seed random number generator
srand(time(0));
// Create a new family with three generations
person *p = create_family(GENERATIONS);
// Print family tree of blood types
print_family(p, 0);
// Free memory
free_family(p);
}
// Create a new individual with `generations`
person *create_family(int generations)
{
// TODO: Allocate memory for new person
person *p = malloc(sizeof(person));
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("Error: not enough memory\n");
return NULL; // ! should be return 1, but it doesn't work
}
// If there are still generations left to create
if (generations > 1)
{
// Create two new parents for current person by recursively calling create_family
person *parent0 = create_family(generations - 1);
person *parent1 = create_family(generations - 1);
// TODO: Set parent pointers for current person
p->parents[0] = parent0;
p->parents[1] = parent1;
// TODO: Randomly assign current person's alleles based on the alleles of their parents
if (rand() % 2)
p->alleles[0] = p->parents[0]->alleles[0];
else
p->alleles[0] = p->parents[0]->alleles[1];
if (rand() % 2)
p->alleles[1] = p->parents[1]->alleles[0];
else
p->alleles[1] = p->parents[1]->alleles[1];
}
// If there are no generations left to create
else
{
// TODO: Set parent pointers to NULL
p->parents[0] = NULL;
p->parents[1] = NULL;
// TODO: Randomly assign alleles
p->alleles[0] = random_allele();
p->alleles[1] = random_allele();
}
// TODO: Return newly created person
return p;
}
// Free `p` and all ancestors of `p`.
int free_family(person *p)
{
// TODO: Handle base case
if (p->parents[0] == NULL && p->parents[1] == NULL)
{
free(p);
return 0;
}
// TODO: Free parents recursively
if (p->parents[0] != NULL)
free_family(p->parents[0]);
if (p->parents[1] != NULL)
free_family(p->parents[1]);
// TODO: Free child
free (p);
return 0;
}
// Print each family member and their alleles.
void print_family(person *p, int generation)
{
// Handle base case
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
// Print indentation
for (int i = 0; i < generation * INDENT_LENGTH; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
// Print person
if (generation == 0)
{
printf("Child (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else if (generation == 1)
{
printf("Parent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < generation - 2; i++)
{
printf("Great-");
}
printf("Grandparent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
// Print parents of current generation
print_family(p->parents[0], generation + 1);
print_family(p->parents[1], generation + 1);
}
// Randomly chooses a blood type allele.
char random_allele()
{
int r = rand() % 3;
if (r == 0)
{
return 'A';
}
else if (r == 1)
{
return 'B';
}
else
{
return 'O';
}
}
Код программы (Штукенция)
// Simulate genetic inheritance of blood type
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
// Each person has two parents and two alleles
typedef struct person
{
struct person *parents[2];
char alleles[2];
}
person;
const int GENERATIONS = 3;
const int INDENT_LENGTH = 4;
person *create_family(int generations);
void print_family(person *p, int generation);
void free_family(person *p);
char random_allele();
int main(void)
{
// Seed random number generator
srand(time(0));
// Create a new family with three generations
person *p = create_family(GENERATIONS);
// Print family tree of blood types
print_family(p, 0);
// Free memory
free_family(p);
}
// Create a new individual with `generations`
person *create_family(int generations)
{
// TODO: Allocate memory for new person
person *new_person = malloc(sizeof(person));
// If there are still generations left to create
if (generations > 1)
{
// Create two new parents for current person by recursively calling create_family
person *parent0 = create_family(generations - 1);
person *parent1 = create_family(generations - 1);
// TODO: Set parent pointers for current person
new_person->parents[0] = parent0;
new_person->parents[1] = parent1;
// TODO: Randomly assign current person's alleles based on the alleles of their parents
new_person->alleles[0] = new_person->parents[0]->alleles[rand() % 2];
new_person->alleles[1] = new_person->parents[1]->alleles[rand() % 2];
}
// If there are no generations left to create
else
{
// TODO: Set parent pointers to NULL
new_person->parents[0] = NULL;
new_person->parents[1] = NULL;
// TODO: Randomly assign alleles
new_person->alleles[0] = random_allele();
new_person->alleles[1] = random_allele();
}
// TODO: Return newly created person
return new_person;
}
// Free `p` and all ancestors of `p`.
void free_family(person *p)
{
// TODO: Handle base case
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
// TODO: Free parents recursively
free_family(p->parents[0]);
free_family(p->parents[1]);
// TODO: Free child
free(p);
}
// Print each family member and their alleles.
void print_family(person *p, int generation)
{
// Handle base case
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
// Print indentation
for (int i = 0; i < generation * INDENT_LENGTH; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
// Print person
if (generation == 0)
{
printf("Child (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else if (generation == 1)
{
printf("Parent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < generation - 2; i++)
{
printf("Great-");
}
printf("Grandparent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
// Print parents of current generation
print_family(p->parents[0], generation + 1);
print_family(p->parents[1], generation + 1);
}
// Randomly chooses a blood type allele.
char random_allele()
{
int r = rand() % 3;
if (r == 0)
{
return 'A';
}
else if (r == 1)
{
return 'B';
}
else
{
return 'O';
}
}