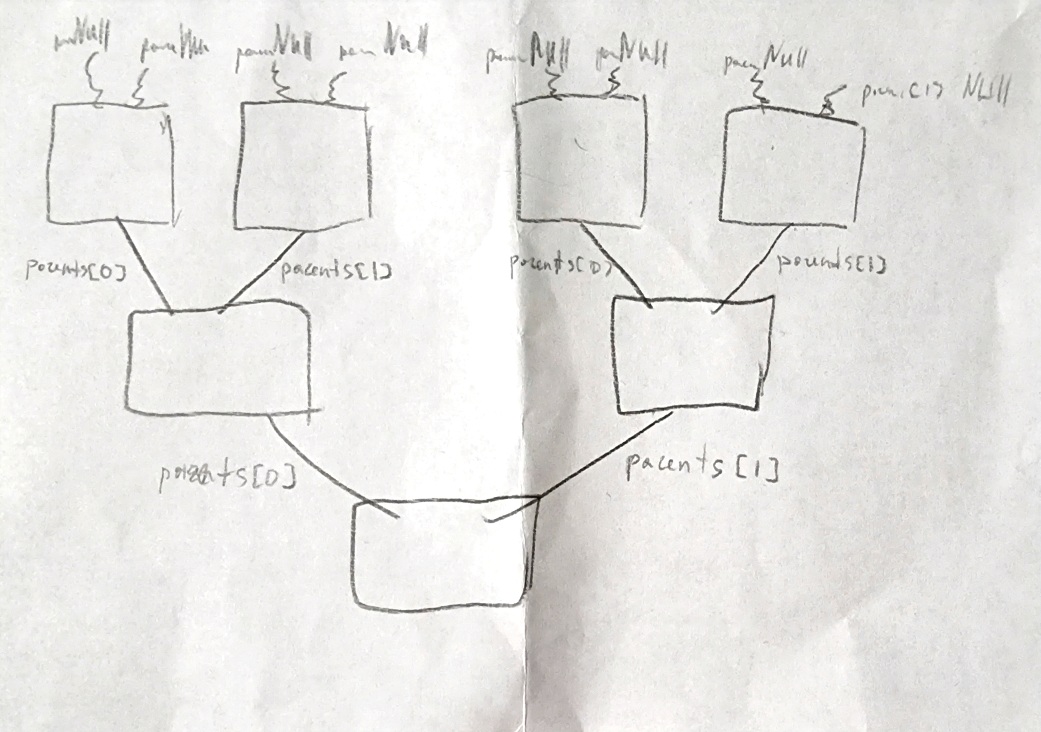
In the fifth week of the Computer Science – CS50 (Harvard) course, we studied data structures and learned how to access structure elements by their address. To complete your homework (Lab 5 – inheritance.c), you need to understand the scientific principle of inheritance of blood type from parents to children. Challenge: Write a program that runs a simulation of a three-generation family and assigns each member a blood type based on the parent’s blood type.
How blood type is inherited:
- there are only three possible forms of the gene (they are called the “allele” or building block) that determine the type of blood group – these are A, B, and O;
the blood type itself is always two alleles (all sorts of combinations of A, B, and O), for example, AO, AA, OB, etc.; - the blood type is “transmitted” from parents to the child as follows: one allele is randomly selected from each parent and then they are combined into a new pair – this is the child’s blood type (for example, the parents had AO and OB -> the child may have AB , OO, OB or AO).
In our task, we need to assign two parents to each child, and so on for three generations. That is, in the younger generation there is a child, he has a mother and father. Mom and dad also have their own moms and dads. The family is created by structure. We were offered a program code where the functions for creating a family and the subsequent clearing of memory are missing.
Program code (igroglaz)
// Simulate genetic inheritance of blood type
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
// Each person has two parents and two alleles
typedef struct person
{
struct person *parents[2];
char alleles[2];
}
person;
const int GENERATIONS = 3;
const int INDENT_LENGTH = 4;
person *create_family(int generations);
void print_family(person *p, int generation);
int free_family(person *p);
char random_allele();
int main(void)
{
// Seed random number generator
srand(time(0));
// Create a new family with three generations
person *p = create_family(GENERATIONS);
// Print family tree of blood types
print_family(p, 0);
// Free memory
free_family(p);
}
// Create a new individual with `generations`
person *create_family(int generations)
{
// TODO: Allocate memory for new person
person *p = malloc(sizeof(person));
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("Error: not enough memory\n");
return NULL; // ! should be return 1, but it doesn't work
}
// If there are still generations left to create
if (generations > 1)
{
// Create two new parents for current person by recursively calling create_family
person *parent0 = create_family(generations - 1);
person *parent1 = create_family(generations - 1);
// TODO: Set parent pointers for current person
p->parents[0] = parent0;
p->parents[1] = parent1;
// TODO: Randomly assign current person's alleles based on the alleles of their parents
if (rand() % 2)
p->alleles[0] = p->parents[0]->alleles[0];
else
p->alleles[0] = p->parents[0]->alleles[1];
if (rand() % 2)
p->alleles[1] = p->parents[1]->alleles[0];
else
p->alleles[1] = p->parents[1]->alleles[1];
}
// If there are no generations left to create
else
{
// TODO: Set parent pointers to NULL
p->parents[0] = NULL;
p->parents[1] = NULL;
// TODO: Randomly assign alleles
p->alleles[0] = random_allele();
p->alleles[1] = random_allele();
}
// TODO: Return newly created person
return p;
}
// Free `p` and all ancestors of `p`.
int free_family(person *p)
{
// TODO: Handle base case
if (p->parents[0] == NULL && p->parents[1] == NULL)
{
free(p);
return 0;
}
// TODO: Free parents recursively
if (p->parents[0] != NULL)
free_family(p->parents[0]);
if (p->parents[1] != NULL)
free_family(p->parents[1]);
// TODO: Free child
free (p);
return 0;
}
// Print each family member and their alleles.
void print_family(person *p, int generation)
{
// Handle base case
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
// Print indentation
for (int i = 0; i < generation * INDENT_LENGTH; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
// Print person
if (generation == 0)
{
printf("Child (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else if (generation == 1)
{
printf("Parent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < generation - 2; i++)
{
printf("Great-");
}
printf("Grandparent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
// Print parents of current generation
print_family(p->parents[0], generation + 1);
print_family(p->parents[1], generation + 1);
}
// Randomly chooses a blood type allele.
char random_allele()
{
int r = rand() % 3;
if (r == 0)
{
return 'A';
}
else if (r == 1)
{
return 'B';
}
else
{
return 'O';
}
}
Program code (Shtukensia)
// Simulate genetic inheritance of blood type
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
// Each person has two parents and two alleles
typedef struct person
{
struct person *parents[2];
char alleles[2];
}
person;
const int GENERATIONS = 3;
const int INDENT_LENGTH = 4;
person *create_family(int generations);
void print_family(person *p, int generation);
void free_family(person *p);
char random_allele();
int main(void)
{
// Seed random number generator
srand(time(0));
// Create a new family with three generations
person *p = create_family(GENERATIONS);
// Print family tree of blood types
print_family(p, 0);
// Free memory
free_family(p);
}
// Create a new individual with `generations`
person *create_family(int generations)
{
// TODO: Allocate memory for new person
person *new_person = malloc(sizeof(person));
// If there are still generations left to create
if (generations > 1)
{
// Create two new parents for current person by recursively calling create_family
person *parent0 = create_family(generations - 1);
person *parent1 = create_family(generations - 1);
// TODO: Set parent pointers for current person
new_person->parents[0] = parent0;
new_person->parents[1] = parent1;
// TODO: Randomly assign current person's alleles based on the alleles of their parents
new_person->alleles[0] = new_person->parents[0]->alleles[rand() % 2];
new_person->alleles[1] = new_person->parents[1]->alleles[rand() % 2];
}
// If there are no generations left to create
else
{
// TODO: Set parent pointers to NULL
new_person->parents[0] = NULL;
new_person->parents[1] = NULL;
// TODO: Randomly assign alleles
new_person->alleles[0] = random_allele();
new_person->alleles[1] = random_allele();
}
// TODO: Return newly created person
return new_person;
}
// Free `p` and all ancestors of `p`.
void free_family(person *p)
{
// TODO: Handle base case
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
// TODO: Free parents recursively
free_family(p->parents[0]);
free_family(p->parents[1]);
// TODO: Free child
free(p);
}
// Print each family member and their alleles.
void print_family(person *p, int generation)
{
// Handle base case
if (p == NULL)
{
return;
}
// Print indentation
for (int i = 0; i < generation * INDENT_LENGTH; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
// Print person
if (generation == 0)
{
printf("Child (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else if (generation == 1)
{
printf("Parent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
else
{
for (int i = 0; i < generation - 2; i++)
{
printf("Great-");
}
printf("Grandparent (Generation %i): blood type %c%c\n", generation, p->alleles[0], p->alleles[1]);
}
// Print parents of current generation
print_family(p->parents[0], generation + 1);
print_family(p->parents[1], generation + 1);
}
// Randomly chooses a blood type allele.
char random_allele()
{
int r = rand() % 3;
if (r == 0)
{
return 'A';
}
else if (r == 1)
{
return 'B';
}
else
{
return 'O';
}
}